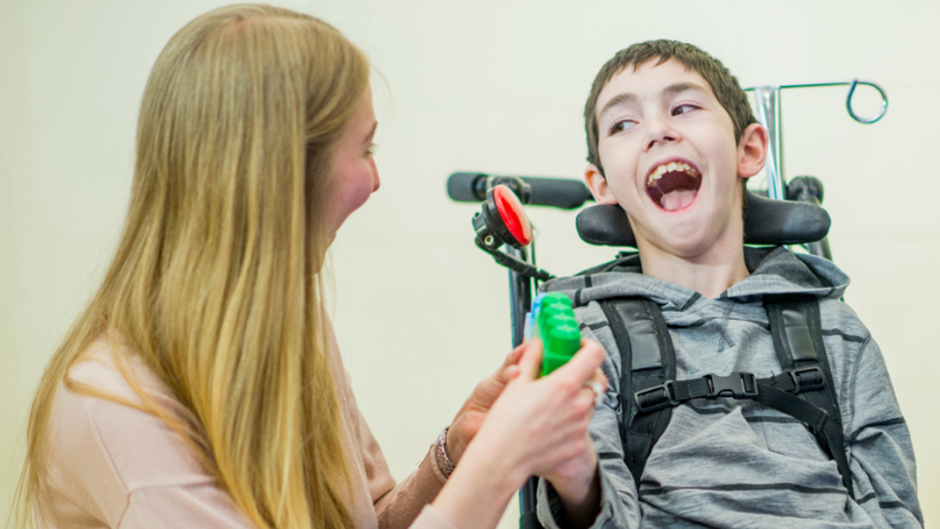
Support networks are crucial for the recovery and well-being of individuals navigating the challenges of traumatic brain injury (TBI). Effective collaboration among families, caregivers, and healthcare professionals significantly influences a survivor’s journey towards rehabilitation. Establishing a strong support system not only provides emotional reassurance but also facilitates access to essential resources and community connections that can enhance the survivor’s quality of life.
TBI survivors often face unique hurdles during their recovery, making a well-rounded support network indispensable. Family members and caregivers play a pivotal role by fostering open lines of communication and encouraging participation in local and online support groups. These connections empower survivors by providing shared experiences, practical advice, and the encouragement needed to face their daily obstacles with resilience.
The recovery process can feel daunting, but it does not have to become a solitary journey. Families who engage actively in their community and focus on collaborative care significantly influence the rehabilitation of TBI survivors. This collective effort leads to improved mental and emotional health, making the path to recovery more manageable and hopeful.
The Role of Families and Caregivers in TBI Recovery
Families and caregivers play a critical role in the recovery journey of individuals who have experienced traumatic brain injury (TBI). Their involvement encompasses various aspects, including emotional support, assistance with daily activities, advocacy in healthcare settings, and collaboration with medical professionals. Each of these elements is pivotal to enhancing recovery and improving quality of life for TBI survivors.
Providing Emotional Support and Encouragement
Emotional support from families and caregivers significantly impacts TBI survivors. The journey post-injury can be fraught with frustration and uncertainty. Caregivers’ patience and understanding encourage survivors to express their feelings and fears.
Support can manifest through active listening and reassurance, which help alleviate feelings of isolation. Celebrating small achievements fosters motivation and reinforces a survivor’s self-esteem. Additionally, caregivers can join support groups to gain insights into their loved one’s experience, enhancing their ability to provide effective emotional backing.
Assisting with Daily Activities and Rehabilitation Exercises
Daily activities can become challenging for TBI survivors due to physical, cognitive, or emotional impairments. Caregivers assist with essential tasks such as grooming, meal preparation, and managing medications. This support not only ensures personal care but also helps maintain a sense of normalcy.
Rehabilitation exercises are crucial for recovery. Caregivers play an important role in guiding TBI survivors through prescribed exercises. They can create structured routines that incorporate these exercises, ensuring consistency. This involvement not only aids physical recovery but also builds a routine that is comforting for the survivor.
Advocating for the Survivor’s Needs Within the Healthcare System
Navigating the healthcare system can be overwhelming for TBI survivors and their families. Caregivers often serve as advocates, ensuring the survivor’s needs are communicated effectively to medical professionals. This includes understanding treatment plans, asking pertinent questions, and seeking second opinions when necessary.
By actively participating in medical appointments, caregivers ensure all concerns are addressed. They can also assist in maintaining comprehensive records of the survivor’s medical history, which can be essential for ongoing care. This advocacy fosters a more supportive environment within the healthcare system, promoting better outcomes for survivors.
Collaboration and Teamwork in the Recovery Process
Collaboration among caregivers, families, and healthcare professionals is vital for optimal TBI recovery. Establishing clear communication channels helps ensure that all parties are aligned on treatment goals. Caregivers can share valuable insights regarding the survivor’s condition, which can inform medical decisions.
Teamwork extends beyond just the immediate family. Involving rehabilitation specialists, therapists, and social workers helps create a comprehensive support network. Regular team meetings can facilitate discussions on progress and adjustments to care plans. Such collaboration enhances the survivor’s journey, making the recovery process more structured and effective.
Key Components of a Strong Support Network
A robust support network is crucial for individuals recovering from traumatic brain injury (TBI).

Such a network encompasses relationships with family and friends, professional healthcare providers, community resources, and online support systems. Each component plays a significant role in addressing the unique challenges faced by TBI survivors and their caregivers.
Family and Friends: Building a Reliable Inner Circle
Family and friends provide essential emotional support to TBI survivors. Their understanding and presence can create a foundation of trust that fosters healing. Maintaining open communication is vital; loved ones should actively listen and encourage the survivor to express their feelings.
Strategies for Building a Supportive Inner Circle:
● Regular Check-Ins: Schedule consistent family gatherings or calls.
● Encourage Participation: Invite friends and family to engage in activities together.
● Educate Them: Share resources about TBI to enhance their understanding.
This inner circle can help ease feelings of isolation and uncertainty, making the recovery journey more manageable and empowering.
Healthcare Professionals: Working with Doctors, Therapists, and Rehabilitation Specialists
Healthcare professionals are integral to a survivor’s recovery, offering tailored rehabilitation strategies. Working closely with doctors, occupational therapists, and speech-language pathologists can address specific cognitive and physical challenges.
Key Roles of Healthcare Professionals:
● Customised Treatment Plans: Develop individualised rehabilitation programs based on assessments.
● Regular Progress Monitoring: Schedule routine follow-ups to assess recovery milestones.
● Cross-Disciplinary Collaboration: Encourage communication between various specialists for a cohesive approach.
A strong relationship with healthcare providers can enhance a survivor’s ability to regain independence and improve overall quality of life.
Community Resources: Accessing Local Support Groups
Community resources play a pivotal role in providing additional support to TBI survivors and their caregivers. Local support groups can foster connections with individuals facing similar challenges, offering shared experiences and coping strategies.
Benefits of Engaging with Community Resources:
● Emotional Support: Provides a safe space to share experiences and feelings.
● Skill Building: Participation can include workshops or activities to enhance skills.
● Information Sharing: Access to valuable information about navigating the recovery process.
Engaging with these resources can alleviate feelings of loneliness and help establish a sense of belonging during the recovery journey.
For caregivers and families, participating in community health programs such as CPR Training Kingston can also be valuable, ensuring they are equipped to respond confidently to medical emergencies that may arise during a TBI survivor’s recovery
Online Communities: Leveraging Virtual Support Networks
Online communities afford TBI survivors and caregivers the opportunity to connect with others across various geographical boundaries. These platforms can offer invaluable sharing of resources, advice, and emotional support in a flexible format.
Advantages of Online Support Networks:
● Accessibility: They can be accessed anytime and anywhere, accommodating varied schedules.
● Diverse Perspectives: Interactions with individuals from different backgrounds enrich understanding.
● Continuity of Support: Online relationships can offer ongoing encouragement throughout the recovery process.
Leveraging these virtual connections can significantly enhance the support network surrounding a TBI survivor, contributing positively to their recovery experience.
How to Connect with Local and Online Resources
Engaging with available local and online resources is essential for TBI survivors and their caregivers. These connections provide valuable information, emotional support, and practical advice tailored to individual needs in the recovery process.
Research Local TBI Support Groups and Organizations
Finding local TBI support groups can significantly benefit survivors and their families. Local organizations often host support meetings, where participants can share experiences and coping strategies. Many communities have dedicated brain injury associations that provide access to resources, education, and advocacy.

Searching online for local support groups is straightforward. Websites like Genesis Community Rehab can offer insights into available services and support networks. Additionally, community health centres may have information on local TBI organizations, making it easier for families to connect with professionals and others facing similar challenges.
Attend Workshops, Seminars, and Community Events
Participating in workshops and seminars can deepen understanding and provide practical skills to aid recovery. Many organizations offer events tailored to TBI, focusing on topics like communication strategies and coping mechanisms.
These gatherings promote learning and create opportunities for building connections with other survivors and caregivers. Community events often feature guest speakers, including healthcare professionals with expertise in brain injury recovery. Attendees can ask questions, receive valuable insights, and develop relationships that support emotional and social well-being.
Online platforms are invaluable for connecting with others affected by TBI. Forums dedicated to brain injury recovery allow individuals to share personal stories, challenges, and successes. Such platforms foster a sense of belonging and reduce the feelings of isolation that survivors may experience.
Social media groups often organize virtual meet-ups and discussions, providing ongoing support and encouragement. Engaging with a broad network of individuals facing similar difficulties allows both survivors and caregivers to access diverse perspectives and resources. This virtual interaction is crucial for creating a supportive community and enhancing emotional health in the recovery process.
The Emotional Impact on Families and Caregivers
The emotional toll of caring for a traumatic brain injury (TBI) survivor can be profound. Caregivers often face stress, burnout, and emotional exhaustion that can affect both their well-being and the recovery of the TBI survivor. Recognizing the need for support and implementing self-care practices can be vital in maintaining balance in this challenging circumstance.
Recognizing Signs of Caregiver Burnout and Stress
Caregiver burnout can manifest in various ways, including fatigue, irritability, and a sense of helplessness. It is crucial for caregivers to identify these signs early, as prolonged stress can lead to serious health issues.
Common symptoms include:
● Withdrawal from social activities
● Frequent feelings of anger or frustration
● Difficulty concentrating or making decisions
● Physical health complaints like headaches or insomnia
Recognizing these signs early can help caregivers seek the necessary support. Acknowledging the stressors related to caregiving and understanding the normalcy of such feelings can make a significant difference in managing their emotional health.
Seeking Emotional Support Through Therapy or Support Groups
Engaging in therapy or joining a support group can provide caregivers with the necessary emotional reinforcement. Professional guidance offers a safe space to express thoughts and feelings, helping caregivers process their experiences.
Support groups can foster connections with others facing similar situations. These groups create a community where caregivers can share their challenges and coping strategies. They may also offer valuable resources and tips for managing the emotional weight of caregiving.
Participating in these avenues leads to increased resilience and can significantly reduce feelings of isolation. Emotional support is not a sign of weakness; instead, it is a healthy approach to coping with the demands of caring for a TBI survivor.
Practising Self-Care to Maintain Mental and Physical Well-Being
Self-care is essential for caregivers to sustain their mental and physical health. Implementing regular self-care routines can help mitigate stress and improve overall well-being.
Important self-care practices include:
● Setting aside time for personal hobbies and interests
● Maintaining social connections with friends and family
● Incorporating physical activity into daily routines
● Ensuring adequate sleep and nutrition
Caregivers should prioritise their needs just as much as those of the TBI survivor. By acknowledging their own needs and seeking balance, caregivers can enhance their ability to provide effective support, contributing to a healthier environment for both themselves and the TBI survivor they care for.
The Long-Term Benefits of a Strong Support Network
A robust support network significantly enhances the recovery journey for traumatic brain injury (TBI) survivors and their families. It fosters improved emotional well-being, encourages a sense of belonging, and facilitates effective navigation through recovery challenges. The following points illustrate the substantial advantages of such networks.
Improved Recovery Progress and Quality of Life for the Survivor
Having a strong support network can lead to tangible improvements in recovery for TBI survivors. Family members, friends, and community resources play a crucial role in providing encouragement and motivation to engage in therapy and rehabilitation exercises.
Support groups can also connect survivors with others who have shared experiences. This interaction can foster a sense of camaraderie and understanding. As survivors feel heard and supported, their motivation to participate in recovery activities often increases, leading to enhanced outcomes.
A structured support system can assist survivors in accessing essential services, such as vocational rehabilitation. This helps them reintegrate into society and pursue educational or employment opportunities. Increased access to resources translates to an overall better quality of life.
Reduced Feelings of Isolation for Both the Survivor and Their Family
Isolation is a common issue faced by TBI survivors and their families. A robust support network significantly alleviates these feelings. Connections with peers who understand the hardships of TBI lead to shared experiences and validation.
Support groups not only benefit survivors but also provide families with insight into caring for their loved ones. Caregivers often face unique challenges and fears; connecting with others in similar situations can offer reassurance and practical advice.
Engaging with a community can also nurture emotional resilience. Members can exchange coping strategies and learn from each other’s experiences. This solidifies a shared sense of purpose and belonging, reducing feelings of loneliness and helplessness among family members.
Recovery from TBI is rarely linear; setbacks often occur. A strong support network equips both survivors and caregivers to handle these challenges more effectively. Through shared understanding, they can collaboratively devise strategies to cope with difficulties as they arise.
Support networks provide practical assistance, such as access to knowledgeable resources or guidance in managing healthcare interactions. Family members can play an essential role in advocating for the survivor’s needs during medical appointments, ensuring that they receive appropriate
Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding the nuances of traumatic brain injury (TBI) recovery is essential for both survivors and their support networks. This section addresses common queries, shedding light on resources available, behavioural changes post-injury, appropriate communication, and the long-term impact of TBI on health and life expectancy.
What resources does the Ontario Brain Injury Association offer to TBI survivors and their families?
The Ontario Brain Injury Association (OBIA) provides comprehensive resources tailored for TBI survivors and their families. They offer a variety of support services, including educational materials, workshops, and access to community programs. These resources aim to inform families about TBI recovery and identify local support systems that facilitate shared experiences and healing.
What behavioural changes are common after sustaining a traumatic brain injury?
Behavioural changes can occur following a traumatic brain injury and may vary from person to person. Survivors might experience mood swings, increased irritability, or difficulty concentrating. Other changes can include impulsivity, social withdrawal, and challenges with emotional regulation. Recognising these changes can help families provide appropriate support and seek necessary interventions.
What should one avoid saying to an individual who has experienced a TBI?
When communicating with someone who has sustained a TBI, certain phrases should be avoided to prevent causing distress or misunderstanding. Statements that belittle their experience, such as “just try to remember” or “it’s all in your head,” can be particularly harmful. Instead, expressing understanding and offering support fosters a more positive and empathetic environment.
How might a traumatic brain injury affect someone’s life expectancy and long-term health?
Traumatic brain injury can have significant implications for life expectancy and long-term health. Individuals with severe TBIs may experience a higher risk of subsequent health issues, including neurological disorders or mental health problems. The degree of recovery often depends on the injury’s severity, individual health factors, and the support provided during rehabilitation, making tailored care crucial for improving outcomes.